
teaching reading to english language learners pdf
Teaching reading to English Language Learners (ELLs) is foundational for their academic success. ELLs often face challenges in decoding, comprehension, and cultural context understanding. A structured approach combining phonics, vocabulary, and comprehension strategies, while incorporating cultural contexts, enhances engagement and proficiency.
1.1 The Importance of Reading Skills for ELLs
Reading skills are crucial for English Language Learners (ELLs) as they form the foundation of academic success. Proficient reading enables ELLs to acquire vocabulary, comprehend complex texts, and bridge language gaps. It fosters cultural understanding and enhances overall communication abilities. Strong reading proficiency boosts confidence and prepares learners for future academic challenges, making it a cornerstone of language acquisition and educational growth.
1.2 Understanding the Challenges ELLs Face in Reading
ELLs often encounter unique challenges in reading, including limited vocabulary, unfamiliar cultural references, and differences in linguistic structures. Decoding difficulties arise from phonetic variations between their native language and English. Additionally, ELLs may struggle with fluency and comprehension due to gaps in prior knowledge and cognitive load. Recognizing these challenges is essential for tailoring instruction to meet their needs and fostering a supportive learning environment.
1.3 Setting Clear Goals for Reading Instruction

Setting clear, achievable goals is crucial for effective reading instruction. Goals should be specific, measurable, and aligned with learners’ needs and language proficiency levels. Incorporating SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) criteria ensures focus and trackability. Aligning goals with educational standards and learners’ interests fosters motivation. Regularly monitoring progress and adjusting instruction helps maintain relevance and accountability, ensuring learners stay on track to improve their reading skills and build confidence in English.

Effective Instructional Strategies
Effective instructional strategies for teaching reading involve interactive activities, group work, and technology integration. Scaffolding techniques and cultural relevance help engage learners and build confidence in reading abilities.
2.1 Phonics Instruction for ELLs
Phonics instruction is crucial for ELLs to decode words effectively. Systematic and explicit teaching of sound-letter relationships helps build foundational reading skills. Visual aids, such as word cards and phonics charts, support learning. Multisensory approaches, like tracing letters while sounding them out, engage multiple learning pathways. Connecting phonics to ELLs’ native language experiences can enhance understanding and reduce confusion. Consistent practice through activities like word sorting and blending games reinforces phonics mastery, enabling ELLs to read unfamiliar words with greater accuracy and confidence.
2.2 Vocabulary Development Techniques
Vocabulary development is vital for ELLs to comprehend texts and express ideas. Explicit instruction using visual aids, real-life examples, and hands-on activities enhances word retention. Pre-teaching high-frequency words and academic vocabulary ensures readiness for reading materials. Encouraging active use through discussions, role-plays, and writing activities reinforces learning. Integrating technology, such as interactive flashcards and word games, makes practice engaging. Connecting new words to ELLs’ prior knowledge and cultural backgrounds fosters deeper understanding and promotes meaningful language acquisition.
2.3 Fluency Practice Methods

Fluency practice methods focus on improving ELLs’ ability to read with accuracy, speed, and expression. Strategies include guided oral reading, where teachers model fluent reading, and repeated reading, allowing ELLs to practice texts multiple times. Audio modeling provides examples of fluent reading for learners to emulate. Technology tools, such as digital readers with adjustable speeds, can enhance practice. Peer reading and small group activities encourage collaborative learning and reduce anxiety, fostering a supportive environment for developing fluency skills effectively.
2.4 Comprehension Strategies
Effective comprehension strategies for ELLs involve teaching techniques to understand and interpret texts. Pre-reading activities, such as previewing content and discussing vocabulary, prepare learners. During reading, strategies like summarizing, questioning, and visualizing help deepen understanding. Post-reading discussions and graphic organizers further reinforce comprehension. Additionally, explicit instruction in identifying main ideas, making inferences, and recognizing text structures enhances ELLs’ ability to engage meaningfully with written content, fostering both language acquisition and critical thinking skills simultaneously.

Technology in Reading Instruction
Technology enhances reading instruction by offering interactive and adaptive resources that provide real-time feedback, engaging English Language Learners and supporting their individual learning needs effectively.
3.1 Digital Tools for Reading Practice
Digital tools like Duolingo, Khan Academy, and Epic! offer interactive reading exercises tailored for ELLs. These platforms provide personalized learning, real-time feedback, and engaging activities that cater to diverse proficiency levels. They incorporate multimedia elements such as audio, visuals, and gamification to make reading practice enjoyable and effective. Additionally, many tools allow teachers to track progress and identify areas needing improvement, ensuring targeted support for each learner’s unique needs.
3.2 Interactive Reading Resources
Interactive reading resources, such as digital books and reading apps, provide ELLs with immersive learning experiences. Tools like Reading A-Z and Starfall offer leveled texts, audio support, and interactive quizzes to reinforce skills. These resources adapt to learners’ proficiency levels, ensuring personalized practice. Multimedia elements, such as animations and videos, enhance engagement and comprehension. Accessible both in class and at home, these tools foster consistent practice and confidence building, making reading a dynamic and enjoyable process for ELLs.
3.3 Personalized Learning Platforms
Personalized learning platforms, such as DreamBox and Reading Horizons, cater to individual ELLs’ needs. These tools use adaptive technology to assess reading levels and deliver tailored content. Real-time feedback and progress tracking help teachers adjust instruction. Interactive activities, games, and multimedia engage learners, fostering independent practice. Data-driven insights enable targeted interventions, ensuring each student progresses at their own pace. These platforms bridge gaps in proficiency, making learning both effective and engaging for diverse ELL populations.

Cultural Considerations
Cultural considerations in teaching reading involve acknowledging learners’ diverse backgrounds and experiences. Using culturally relevant texts and practices helps ELLs connect with material, fostering engagement and understanding.
4.1 Incorporating Cultural Contexts in Reading Materials
Incorporating cultural contexts in reading materials helps ELLs connect with the content on a personal level. Using texts that reflect diverse cultures and experiences can enhance comprehension and engagement. Teachers should select materials that align with learners’ backgrounds while introducing new cultural perspectives. This approach fosters inclusivity and promotes cross-cultural understanding. Additionally, culturally responsive materials can validate students’ identities, making the learning environment more welcoming and effective for language acquisition.
4.2 Creating a Culturally Responsive Classroom Environment
Creating a culturally responsive classroom environment involves fostering respect for all students’ backgrounds. Teachers should display diverse texts, images, and materials reflecting learners’ cultures. Encouraging discussions about cultural differences and similarities promotes inclusivity. Using students’ native languages alongside English and adapting instructional strategies to meet diverse learning styles also supports a culturally responsive environment. This approach ensures students feel valued, building confidence and motivation in their reading and language development.
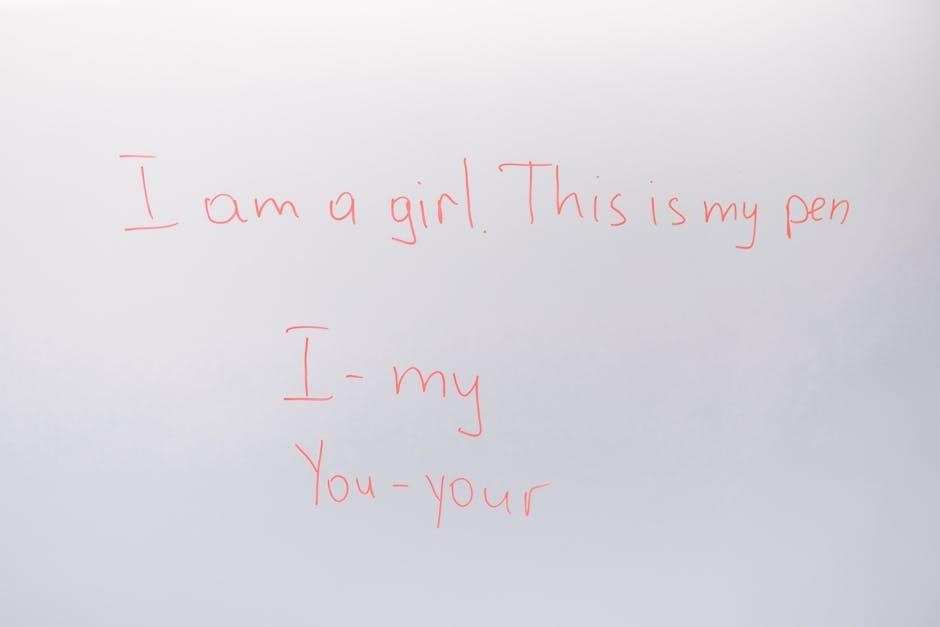
Creating an Engaging Reading Environment
Arrange the classroom to promote interaction, ensuring easy access to materials. Incorporate technology, like interactive reading tools, to enhance engagement and cater to different learning preferences effectively.
5.1 Classroom Setup for Reading Activities
Arrange the classroom to promote interaction and comfort. Use group settings for collaborative reading, ensure easy access to materials, and incorporate technology. A quiet, well-lit environment with flexible seating and cultural displays enhances engagement. Utilize visual aids and graphic organizers to support comprehension. Ensure materials are organized by difficulty and topic, fostering a welcoming and inclusive space that aligns with reading goals, such as fluency and comprehension, while allowing for adaptability and easy monitoring of student progress.
5.2 Encouraging Student Participation
Encourage active participation by creating a supportive environment where ELLs feel comfortable sharing ideas. Use interactive activities like group reading, role-playing, and discussions to engage students. Provide positive reinforcement and constructive feedback to build confidence. Incorporate culturally relevant texts to connect with learners’ backgrounds. Encourage peer-to-peer interaction to foster collaboration and language practice. Offer choice in reading materials to increase motivation and personal interest, ensuring all students feel valued and involved in the learning process.
Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated instruction tailors reading lessons to meet diverse learner needs, ensuring ELLs receive targeted support. Strategies include leveled texts, flexible grouping, and technology integration to enhance engagement and progress.
6.1 Tailoring Instruction to Learner Needs
Tailoring reading instruction to meet individual ELL needs is crucial for effective learning. Assessing each student’s language proficiency, reading level, and learning style helps create personalized plans. Implementing strategies like scaffolding, visual aids, and interactive activities ensures comprehension and engagement. By addressing diverse abilities and backgrounds, teachers can foster a supportive environment that promotes progress and confidence in reading skills.
6.2 Grouping Strategies
Effective grouping strategies enhance reading instruction for ELLs by catering to diverse needs. Pairing students with similar proficiency levels or mixed abilities fosters collaboration and peer support. Small groups allow for targeted instruction, while whole-class activities promote shared learning experiences. Flexible grouping ensures that students receive tailored practice, improving engagement and progress in reading skills.

Parental Involvement
Engaging parents in their children’s reading development fosters a supportive learning environment. Providing resources for home practice strengthens literacy skills and promotes consistent progress in reading proficiency.
7.1 Engaging Parents in Reading Development
Engaging parents in reading development is crucial for ELLs’ success. Schools can host reading workshops, demonstrating strategies like phonics and vocabulary building. Providing bilingual resources and setting achievable goals encourages parental involvement. Regular communication through newsletters or apps keeps parents informed. Encouraging daily reading at home, even in the native language, reinforces skills. Celebrating progress through parent-teacher conferences or reading events fosters motivation. This collaborative approach creates a supportive learning environment, bridging school and home efforts.
7.2 Providing Resources for Home Practice
Providing resources for home practice strengthens ELLs’ reading skills. Schools can supply bilingual books, interactive reading apps, and online platforms. Printable worksheets and audio materials also support independent learning. Offering culturally relevant texts ensures engagement. Parents can benefit from guides on creating a reading-friendly home environment. Regular updates and access to digital libraries further enhance practice opportunities. These resources empower families to actively contribute to their children’s reading development, fostering consistent progress and a love for learning.

Continuous Professional Development
Continuous professional development is essential for educators to stay updated on best practices in teaching reading to ELLs. By leveraging effective search strategies and resources, teachers can enhance their instructional methods and improve student outcomes through ongoing learning and collaboration.
8.1 Staying Updated on Best Practices
Educators must stay informed about the latest research and methodologies in teaching reading to ELLs. By utilizing advanced search strategies, such as Boolean operators and phrase searching, teachers can efficiently locate relevant resources. Leveraging digital tools, attending webinars, and participating in professional networks provide opportunities for continuous learning. Incorporating these practices ensures educators adopt evidence-based methods, fostering improved outcomes for ELLs in reading instruction.
8.2 Collaborative Teaching Approaches
Collaborative teaching approaches enhance reading instruction for ELLs by fostering teamwork among educators. Strategies like co-planning, team-teaching, and peer coaching ensure aligned instruction. Professional learning communities provide platforms for sharing best practices, while resource sharing and cross-disciplinary collaboration enrich lesson design. Such approaches promote consistency, creativity, and targeted support, ultimately benefiting ELLs’ reading development and overall academic growth.